Let’s face it—the word “taxes” alone can be a major stress inducer for most people. A main reason for this is the underlying fear of making a mistake that could lead to an IRS audit, potentially resulting in hefty fines, penalties, or even a jail sentence. In the past three years, there have been more than 5,000 investigations of tax crimes in the United States. In 2019, investigations led to nearly 850 jail sentences.
But how does one become a target of the IRS? First, we need to explore the differences between tax evasion and tax avoidance. Although these terms are often used interchangeably, they are starkly different concepts that carry different legal implications.
Tax Evasion
What is it?
Tax evasion is the act of using illegal means in order to deliberately avoid paying taxes. This typically includes the willful attempt of hiding or falsifying income. Common examples of tax evasion include:
- Underreporting income
- Claiming false expenses and/or deductions
- Knowingly underpaying taxes
- Hiding income sources
- Refusing to file your tax return altogether
Who’s at risk?
In a general sense, the IRS does not go after those who cannot pay their taxes due to a lack of funds. Additionally, the IRS is highly skilled in determining if a tax misrepresentation was simply a mistake or due to purposeful evasion. After all, they know as well as anyone the intricate laws, complicated math, and risk of human error that go hand-in-hand with filing taxes. Rest easy knowing that honest mistakes or negligence do not constitute tax evasion.
The legal trouble can begin when there is a deliberate act of deceit to reduce the amount of taxes you owe. To determine what is considered “willful,” the IRS typically looks for substantial discrepancies over several years to demonstrate a repeated pattern of behavior.
However, it is important to remain diligent to avoid potentially making a large, long-term mistake without even realizing it. A good example of this is not reporting income from a side business. Failure to do so (for instance, not reporting cash transactions from a side gig) has gotten many independent contractors into hot water with the IRS.
What are the potential legal consequences?
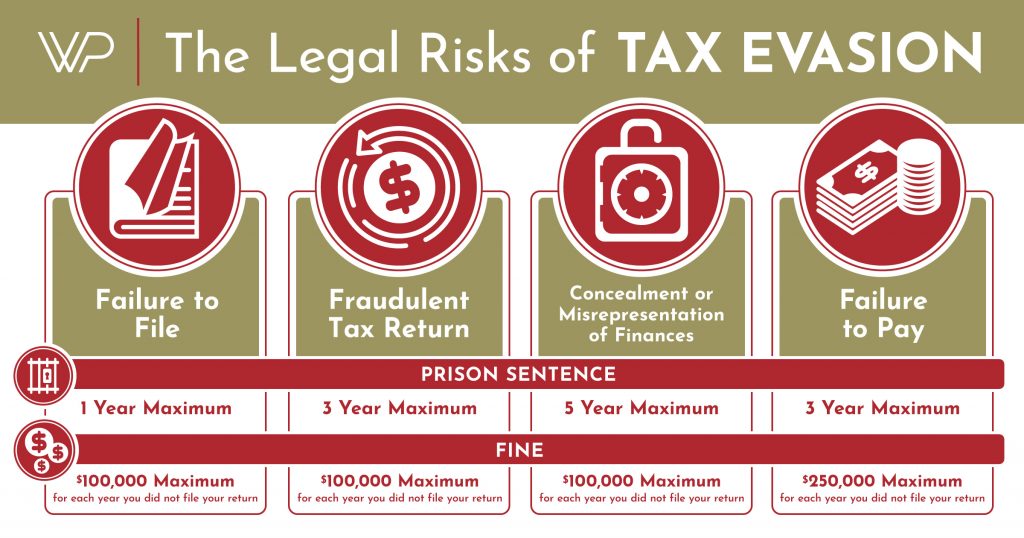
Willfully failing to pay taxes is a federal offense under the IRS tax code. Citizens who are caught for tax evasion are typically subject to criminal charges, substantial fines, and even prison time. Depending on the act committed, the legal risks include:
- Failure to file
-
- Prison Sentence: Maximum one year
- Fine: Maximum $100,000 for each year you did not file your tax return
- Fraudulent tax return
- Prison Sentence: Maximum three years
- Fine: Maximum $100,000
- Concealment or misrepresentation of finances
- Prison Sentence: Maximum five years
- Fine: Maximum $100,000
- Failure to pay
- Prison Sentence: Maximum three years
- Fine: Maximum $250,000
What is Tax Avoidance?
Tax avoidance, on the other hand, is perfectly legal. Tax avoidance is the act of minimizing the amount of what is owed by using loopholes that exist within the code. Common examples of tax avoidance include:
- Utilizing legitimate tax deductions
- Using a tax deferral plan, such as 401(k), IRA, or SEP-IRA
- Employing tax credits for legitimate purposes
Who’s at risk?
As we mentioned, employing acts of tax avoidance is legal. However, certain strategies can become risky and have consequences if not executed carefully.
For example, a tax loophole falls under the umbrella of tax avoidance. A tax loophole is a provision under the current law that allows taxpayers to reduce their liability. Because the tax code is so complex, tax loopholes inherently exist as it is virtually impossible to detail every possible scenario. Instead, taxpayers find savvy ways to take advantage of lower taxes without breaking the law.
Additionally, another strategy that falls under tax avoidance is tax shields. A tax shield is the reduction in taxable income by claiming allowable deductions. Deductions could include charitable donations, medical expenses, mortgage interest, depreciation, and more.
What are the potential legal consequences?
While tax avoidance, tax loopholes, and tax shields are all legal, the more complex you make your approach the more risk you add. If you are considering utilizing a tax loophole, for example, it is important that you consult with a tax professional for expert advice. Failure to do so could result in crossing the fine line from tax avoidance to tax evasion, which carries the legal risks detailed above.
When to Consult a Lawyer
Because tax fraud can result in life-altering consequences such as heavy fines and imprisonment, it is not a situation that should be taken lightly. As we’ve learned, if you have completed your tax returns in good faith, it is not likely you will be a target of an IRS audit. However, if you do find yourself under audit by the IRS or (worse) charged with a tax fraud crime, it is imperative to contact a skilled attorney.